What’s Going On Inside Your Child’s Brain?
Children vs Adult Brains:
A child’s brain has completely different priorities than an adults.
Children think, behave, and learn differently —
Meaning parenting and teaching can be a challenge
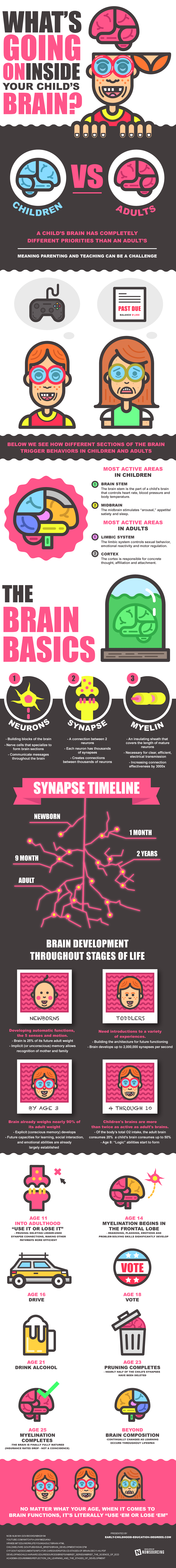
Below we see how different sections of the brain trigger behaviors in children and adults.
Most active areas in children:
1. Brain stem
The brain stem is the part of a child’s brain that controls heart rate, blood pressure and body temperature.
2. Midbrain
The midbrain stimulates “arousal,” appetite/ satiety and sleep.
Most active areas in adults:
1. Limbic system
The limbic system controls sexual behavior, emotional reactivity and motor regulation.
2. Cortex
The cortex is responsible for concrete thought, affiliation and attachment.
The Brain Basics
1. Neurons:
- Building blocks of the brain
- Nerve cells that specialize to form brain sections
- Communicate messages throughout the brain
2. Synapse:
- A connection between 2 neurons
- Each Neuron has thousands of synapses
- Creates connections between thousands of neurons.
3. Myelin:
- An insulating sheath that covers the length of mature neurons
- Necessary for clear, efficient, electrical transmission
- Increasing connection effectiveness by 3000x
Synapse Time Line
Brain development throughout stages of life:
[Newborns]
- Developing automatic functions, the 5 senses, and motion
- Brain is 25% of its future adult weight
- Implicit (or unconscious) memory allows recognition of mother and family
[Toddlers]
- Brain develops up to 2,000,000 synapses per second
- Building the architecture for future functioning
[by Age 3]
- Brain already weighs nearly 90% of it’s future adult weight
- Explicit (conscious memory) develops
- Future capacities for learning, social interaction, and emotional abilities are already largely established
[4 through 10 ]
- Children’s brains are more than twice as active as adult’s brains.
- Of the body’s total O2 intake, the adult brain consumes 20%A child’s brain consumes up to 50%
[by Age 8]
- “Logic” abilities start to form
[Age 11 into adulthood]
- “Use it or Lose it”
- Pruning: deleting lesser-used synapse connections making other pathways more efficient
[Age 14]
- Myelination begins in the Frontal Lobe (higher learning)
- Reasoning, planning, emotions, and problem-solving skills significantly develop
[Age 16] Drive a car
[Age 18] Vote
[Age 21] Drink Alcohol
[Age 23]
- Pruning completes
- Nearly half of the child’s synapses have been deleted
[Age 25]
- Myelination completes
- The brain is finally fully matured
Insurance rates drop – Not a coincidence
[Beyond:]
- Brain Composition
- Continually changes as learning occurs throughout lifespan
No matter what your age, when it comes to brain functions, it’s literally “use ’em or lose ’em”
Sources:
http://developingchild.harvard.edu/resources/briefs/inbrief_series/inbrief_the_science_of_ecd
http://www.cyf.govt.nz/documents/info-for-caregivers/fds-cd-stages-of-brain-dec11-hu.pdf
http://hrweb.mit.edu/worklife/youngadult/brain.html
http://www.academia.edu/6089683/REFLECTION_ON_LEARNING_AND_THE_STAGES_OF_DEVELOPMENT
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jXnyM0ZuKNU
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK28194